Viral diseases are widespread infections often caused by virus microorganisms. This article will discuss common types of viral diseases and their treatment.
What Is A Virus?
A virus is a tiny particle of genetic material, either DNA or RNA, surrounded by a protein coat. Some viruses have fatty envelope covers and are incapable of replicating alone. They often depend on their hosts for survival.
The virus has a bad reputation, but it also has a crucial function for humans, plants, animals, and the environment. Some viruses participate in the evolution process, and they sometimes protect the host against other infections.
On the negative side, viruses can affect the liver, brain, and skin. Research shows that it can cause complications in many cancers and viral diseases.
Millions of different viruses may exist, but researchers have only identified 219 species that can infect humans. Despite how widespread they are, 92% of Australians don’t know the difference between viral diseases and bacterial infections.
4 Common Viral Diseases
Viral infections are responsible for many diseases, and some can potentially be fatal. The most common ones affecting humans are the flu, chickenpox, acute bronchitis, and HIV and AIDS.
The Flu
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is a viral infection that attacks a person’s respiratory system. There are two types of viruses that cause epidemics every year – influenza A and B.
Symptoms of flu may include runny nose, sneezing, and sore throat. The person may also develop a high fever and suffer from body aches, pain, and weakness.
A person suffering from flu symptoms will need to get plenty of rest and maintain a high fluid intake. Small children, pregnant women, and those with weak immune systems are at greater risk of this viral infection.
Consult a doctor if symptoms worsen, or to plan ahead and get a vaccine against this viral disease.
Chickenpox
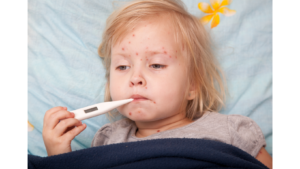 Chickenpox is from the varicella-zoster virus, which is another common viral disease. The best known symptom is the appearance of red spots all over the body, which can be filled with fluids and may convert into blisters.
Chickenpox is from the varicella-zoster virus, which is another common viral disease. The best known symptom is the appearance of red spots all over the body, which can be filled with fluids and may convert into blisters.
Symptoms can start developing in the first two days of exposure to the virus. The person may experience low-grade fever, headaches, fatigue, and loss of appetite.
There is no formal treatment for chickenpox, and the recovery may take up to 10 to 15 days. However, the person can take over-the-counter medications (such as acetaminophen) and apply cooling creams and topical ointment to relieve the itching.
Acute Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is a viral infection with similar symptoms to colds and the flu. It is characterized by the inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are responsible for carrying air into the lungs.
Infection to these tubes may cause them to swell and form mucus inside. Narrowing of airways can make it harder for the person to breathe.
First aid treatment for acute bronchitis may involve taking medications to control symptoms. Drink plenty of fluids and treat cough and fever. Most cases typically go away within 7 to 10 days.
HIV And Aids
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus, which attacks the body’s immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to acquired immunodeficiency syndrome or AIDS.
HIV is responsible for infecting and killing the T-cells, which helps the body fight against pathogens. As a result, the body becomes vulnerable to certain types of diseases.
A person can get HIV when transmitted by blood, breast milk, semen, and other bodily fluids. There is no permanent cure for this virus as of today, but with proper care, you can control the symptoms.
The Bottom Line
Countless viral diseases afflict people every day. The body’s immune system can fight off these infections in most cases.
If you are suffering from viral disease, be sure to get enough rest and drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration. Take medications and stay away from others in the meantime. These measures can help alleviate the symptoms and speed up the healing process.
First Aid And Viral Diseases
When providing care to someone with viral diseases, consider how to lessen the risk of infection. Without extra precautions, there is risk of becoming sick yourself. But this doesn’t mean you shouldn’t be willing to help a person who is ill if it’s is safe to do so.
Providing first aid (especially if someone is unresponsive and isn’t breathing), can dramatically increase their chance of survival.
Learn first aid today and help combat the adverse effects of viral diseases.