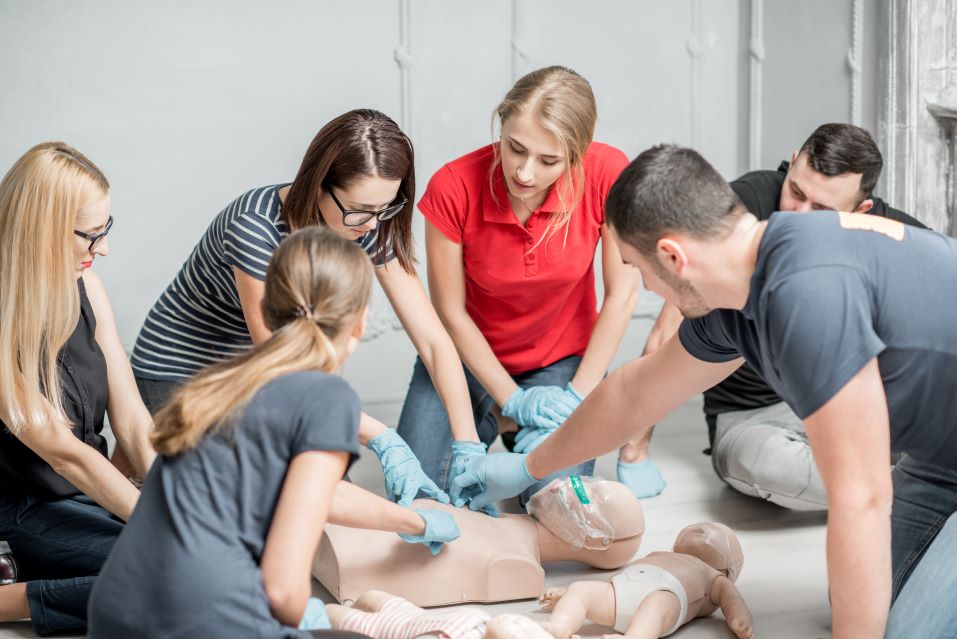
The first five minutes after a sudden cardiac arrest are the most critical. Administering CPR help keep the blood flowing to vital organs of the body, including the brain. It prevents brain death and gives the person a better chance of having a full recovery.
CPR is an essential skill that everyone can learn. Read on to know different resuscitation techniques, along with some tips when it comes to saving lives.
What Is CPR?
CPR is a first-aid technique given to a person who is not breathing or has no pulse. It is a valuable technique in many emergencies, such as heart attacks and near-drowning.
CPR keeps oxygen-rich blood flowing to the brain and other organs until the heart restores its normal function. Without prompt and effective resuscitation, irreversible brain damage can occur in a matter of minutes.
Approximately 25,000 Australians suffer from out of hospital cardiac arrest in any given year, but the overall survival rate is only less than 10%. The good news is the performance of CPR in a timely and effective manner can significantly improve one’s chance of survival.
The report states that by performing CPR in the first few minutes of the attack, chances of survival will increase by 75 per cent.
Guide On How To Perform CPR
The three main resuscitation processes include clearing the airway, mouth to mouth breathing, and chest compressions. For easy recollection, use the letters C-A-B which stands for Compressions, Airway, and Breathing.
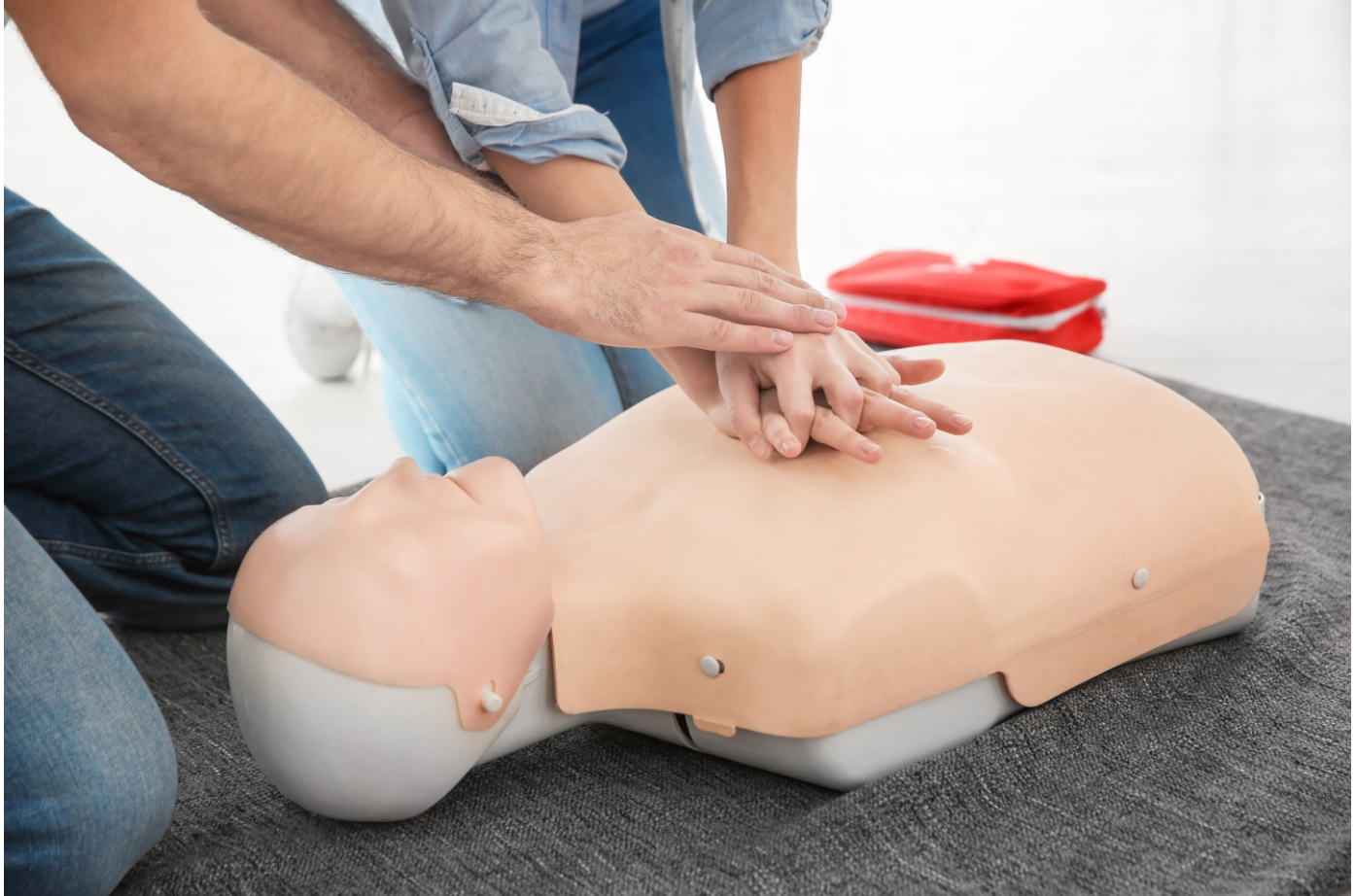
For Untrained Bystanders:
Bystanders who do not undergo formal CPR training should provide hands-only resuscitation. It also applies to those who have training but are rusty in technique. Hands-only CPR is resuscitation without rescue breathes that translates to 100 to 120 uninterrupted chest compressions per minute. Do this in cycles until emergency help arrives.
For Trained And Ready To Go Bystanders:
Bystanders who undergo formal training are mostly confident in their capabilities. Start by checking the person’s breathing and pulse. If the victim shows no signs of breathing or pulse, start chest compressions. Perform 30 chest compressions and give two mouth-to-mouth rescue breathes alternatively until emergency help arrives.
For Trained But Rusty Bystanders:
Bystanders who received previous CPR training but are not confident in delivering this technique should do chest compressions only. Do it at a rate of 100 to 120 chest compressions per minute.
The above advice on resuscitation techniques only applies to adult and children who needs CPR. A different procedure applies to Infants and new-borns up to 4 weeks old.
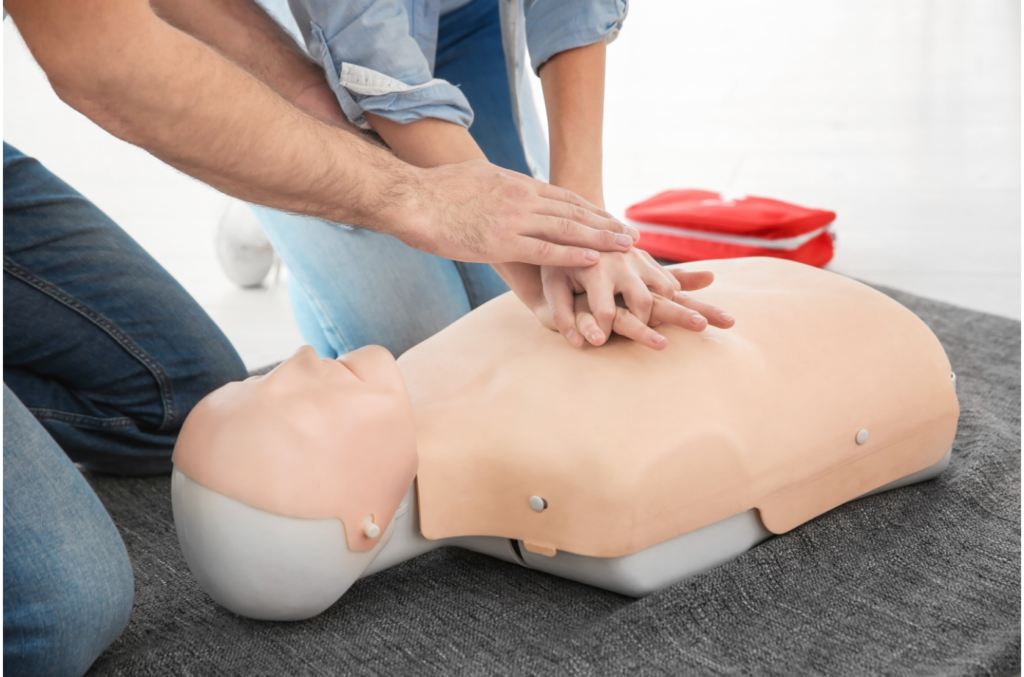
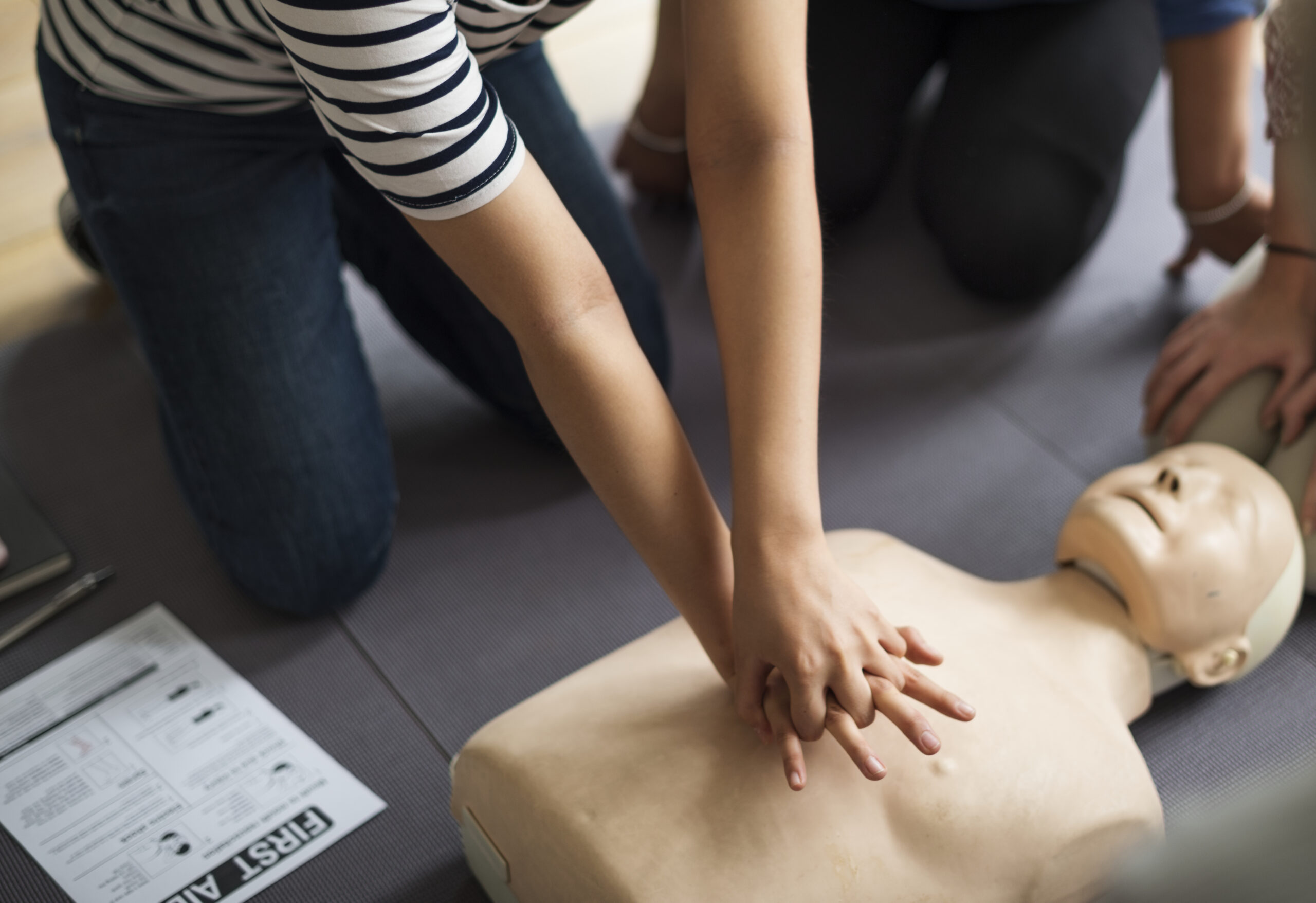
Guide On Chest Compressions
- Place the casualty on their back.
- Put the heel of the hand on the centre chest, near the lower half of the breastbone. Place the other hand on the top of the first hand and interlock the fingers.
- Keep the arms straight and start pressing down on the person’s chest by one-third of the chest depth.
- Release the pressure. Press down, and release is equivalent to one compression.
Guide On Rescue Breathing
- Open the person’s airway by gently tilting their head and chin backwards.
- Pinch the soft part of the person’s nose and close it using the index finger and thumb.
- Take a steady deep breath and place your mouth over the person’s mouth, ensuring a good seal. Blow steadily and watch for the chest to rise.
- Monitor the person’s chest movements. Look and feel if the air expells from the lungs.
- Do it in a cycle with chest compressions with a ratio of 30:2 – 30 compressions followed by two rescue breaths. Do it many times until emergency help is ready to take over.
CPR Training
CPR classes provide the skills and confidence needed to transform one individual from a bystander to a lifesaver. CPR certification ensures a person has the necessary training to make the right decision in an emergency.
By nature, resuscitation classes are hands-on and interactive. Participants will learn how to properly perform chest compressions and rescue breaths in a fun and supportive environment.
Enrol in a CPR course for more information.